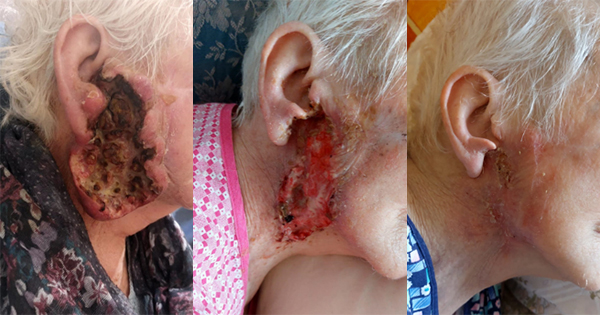
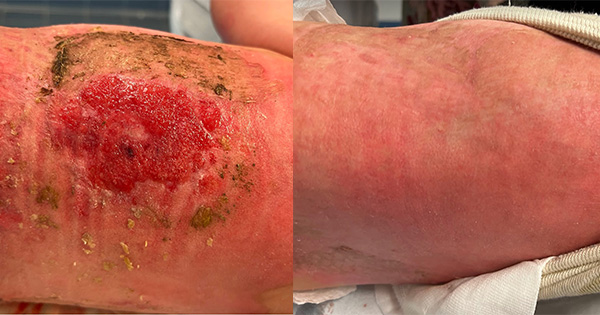
Beta-haemolytic Streptococcus is a Gram-positive microorganism that is found in burn wounds and provokes graft failure. Streptococcus pyogenes toxins increase the depth and severity of burn wounds. Topical antimicrobial agents can be used to treat burn wounds and improve results after burn infection. However, there are few studies exploring the antimicrobial action of silver sulfadiazine against S pyogenes. This study aimed to evaluate 1% silver sulfadiazine antimicrobial activity against S pyogenes. We isolated eight S pyogenes samples from adult patients at the Hospital Provincial de Rosario, Rosario, Argentina. Six samples were from burn wounds and two from blood culture. The outcomes were compared with the topical antimicrobial agents 2% mupirocin and 1% fusidic acid cream. We tested and compared the susceptibility of S pyogenes with these topical antimicrobial agents using agar well diffusion assays and minimum bactericidal concentration tests. The results show that the 1% silver sulfadiazine cream has an inhibitory effect on S pyogenes similar to that of 2% mupirocin and 1% fusidic acid cream. Considering its greater antimicrobial spectrum, silver sulfadiazine is a valid alternative to control many infections associated with wounds and burns, including those caused by S pyogenes.