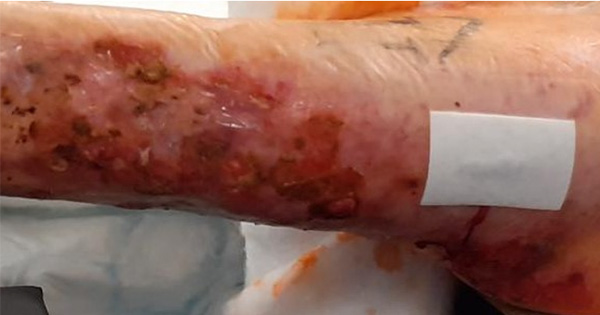
<p>Individuals presenting with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) — an autoimmune disease with prothrombotic condition — have a high incidence of recurrent thrombosis. In many cases, anticoagulation therapy cannot be avoided, however, the nature of this therapy remains controversial. This case study describes a female patient with APS associated with recurrent thrombosis and haematoma formation that resulted in multiple skin necrosis. In this case, debridement of necrotic tissue was undertaken and when this did not heal the wound, negative pressure wound therapy was initiated, which was successful in achieving wound closure.</p>