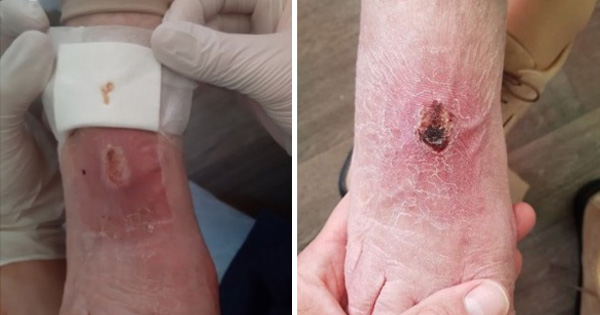
Surgical wound dehiscence (SWD) is almost certainly under-reported, not least because of variation in the interpretation of what constitutes SWD. As a result, patients with SWD may not receive optimal treatment and may experience additional surgical site complications, increased mortality, prolonged hospital stays and readmission. Following a meeting in July 2017, an international panel of clinical experts developed a consensus document to raise awareness of SWD, to aid identification of patients at increased risk and to provide practical guidance in prevention and management. This document has the endorsement of the World Union of Wound Healing Societies (WUWHS) and ultimately aims to improve outcomes for patients.
Supported by Smith & Nephew